Overview of Alumina Ceramic Materials
Alumina ceramic is a ceramic material with α-Al2O3 as the main crystalline phase. It is not only inexpensive and readily available, but also possesses high mechanical properties, high electrical insulation, and low dielectric loss. In practical engineering applications, alumina ceramics generally have an Al2O3 content between 75% and 99.9%. Different Al2O3 content results in different properties and applications.
Advantages of alumina ceramics
Alumina ceramics possess high mechanical strength, high volume resistivity, excellent electrical insulation properties, high hardness, wear resistance, and oxidation resistance. They are widely used as structural components and functional ceramic parts, such as wear-resistant and corrosion-resistant components in mechanical and chemical industries; crucibles, protective tubes, and refractory materials; and electronic components such as substrates, insulators, radar radomes, and microwave dielectrics. Alumina ceramics are one of the earliest studied, widely applied, and relatively mature advanced ceramics.

Crystalline forms of aluminum oxide
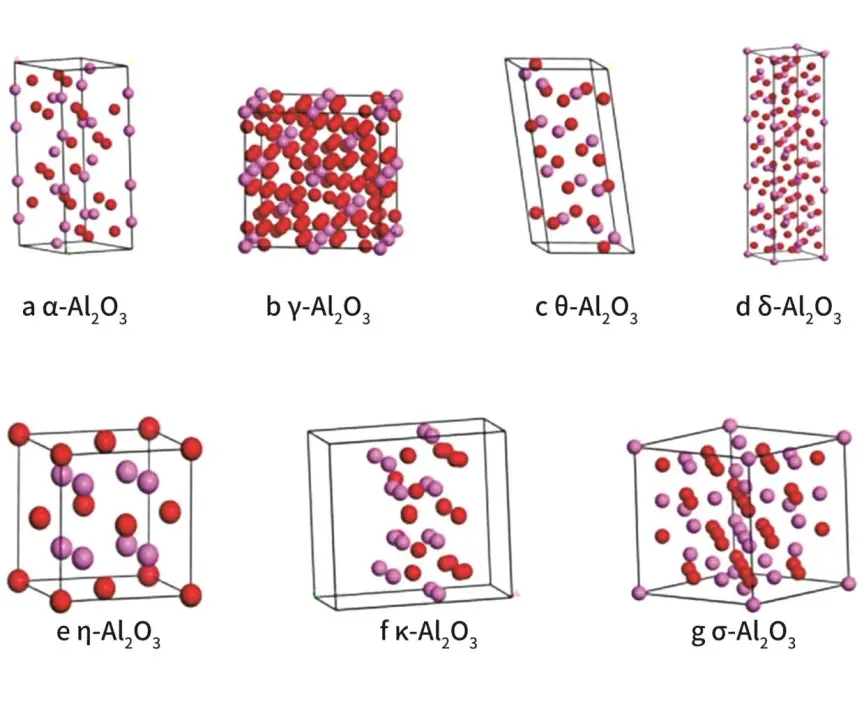
Aluminum oxide (Al₂O₃) is known to exist in more than ten crystalline structures, including α, γ, β, η, δ, θ, χ, κ-Al₂O₃ and an amorphous phase. Among these, the most common and important are α-Al₂O₃, γ-Al₂O₃, and β-Al₂O₃. These different forms of aluminum oxide exhibit significant differences in structure and properties, which determine their respective application areas.
α-Al2O3 has a trigonal crystal system, the most compact structure, low chemical activity, good high-temperature stability, excellent electrical properties, and the best mechanical properties.
β-Al2O3 is a polyaluminate mineral with a very high Al2O3 content. Its chemical composition contains a certain amount of alkaline earth metal oxides and alkali metal oxides, and it can also exhibit ionic conductivity.
γ-Al2O3 has a spinel-type cubic structure. It is unstable at high temperatures and has poor mechanical and electrical properties. However, it has a high specific surface area and strong chemical activity, and can be used as an adsorbent material after technical improvements.
Alumina ceramics, with α-Al₂O₃ (corundum phase) as the sole main crystalline phase, possess high hardness, high-temperature stability, and excellent electrical insulation properties, making them the preferred material for wear-resistant, structural, and electronic ceramics.
Properties of Al2O3 Ceramics
Al2O3 ceramics have a wide range of applications. Due to the different Al2O3 content, their properties and uses vary accordingly.
| Al₂O₃ Purity | Material Type | Key Characteristics | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| ≥ 99.9% | Ultra High-Purity Alumina | Extremely high electrical insulation, excellent chemical purity, superior thermal stability, low dielectric loss | Semiconductor components, electronic substrates, optical and laser components, high-voltage insulation |
| 99.5% – 99.9% | High-Purity Alumina | High mechanical strength, excellent wear resistance, good thermal conductivity, high dielectric strength | IC substrates, electronic packages, precision insulators, medical and laboratory components |
| 99% | Engineering Alumina | Balanced mechanical strength and cost efficiency, good wear and corrosion resistance | Mechanical seals, bearings, valve components, industrial wear parts |
| 96% – 98% | Technical Alumina | High hardness, good electrical insulation, cost-effective, easy to process | Electrical insulators, ceramic tubes, bushings, structural components |
| 92% – 95% | Industrial Alumina | Moderate strength, good thermal shock resistance, economical material choice | Furnace parts, thermal insulation components, refractory supports |
| ≤ 90% | Low-Purity Alumina | Higher porosity, lower mechanical strength, improved thermal insulation | Kiln furniture, heat shields, filtration supports, non-critical structural parts |
Jifeng Ceramic Materials Performance Table
| Property | Unit | A-100 | A-200 | A-300 | AZ-100 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Material | – | 97% Al2O3 | 99.5% Al2O3 | 99.7% Al2O3 | ZrO2 / Al2O3 |
| Colour | – | White ivory | Ivory White | White | White |
| Density | g/cm³ | 3.75 | 3.9 | 3.92 | 4.2 |
| Flexural Strength | MPa | 280 | 370 | 320 | 480 |
| Compressive Strength | MPa | 2250 | 2300 | 2450 | 2700 |
| Modulus of Elasticity (Young’s) | GPa | 330 | 380 | 370 | 350 |
| Fracture Toughness | MPa·m1/2 | 3 | 4.5 | 4 | 5.5 |
| Poisson’s Ratio | – | 0.23 | 0.22 | 0.22 | 0.24 |
| Hardness | HRA | 90 | 91 | 91 | 91 |
| Vickers Hardness | HV1 | 1450 | 1550 | 1600 | 1600 |
| Thermal Expansion Coefficient | 10-6/K | 7.1 | 6.8 | 6.8 | 9.2 |
| Thermal Conductivity | W/mk | 25 | 32 | 32 | 8 |
| Thermal Shock Resistance | – | 200 | 220 | 220 | 470 |
| Max Use Temp (Oxidizing) | °C | 1200 | 1400 | 1650 | 1000 |
| Max Use Temp (Inert) | °C | 1200 | 1400 | 1700 | 1000 |
| Volume Resistivity (20°C) | Ω·cm | 1014 | 1015 | 1015 | 1014 |
| Dielectric Strength | kV/mm | 16 | 20 | 20 | 16.5 |
| Dielectric Constant (1MHz) | – | 11.5 | 11 | 10 | 11 |
| Dielectric Loss Angle (20°C, 1MHz) | tanδ | 3×10-3 | 1×10-3 | 1×10-3 | 2×10-2 (9GHz) |
How are alumina ceramics manufactured?

Based on product performance requirements (such as mechanical strength, insulation, and thermal conductivity), alumina powder of the appropriate purity and specifications is selected. Through ball milling and mixing, adding trace amounts of performance modifiers, and then spray granulation, free-flowing spherical particles are obtained, preparing them for subsequent molding.
- The forming technique is selected based on the product shape and requirements, including dry pressing, isostatic pressing, injection molding, and tape casting.
- The core objective is to ensure uniform green body density and prevent cracking or deformation during sintering due to stress concentration.
- This is a crucial step in achieving the final performance of the material. The process involves debinding to remove organic binders, followed by sintering at high temperatures. This process requires precise control of the heating curve, holding time, and cooling rate to densify and bond the powder particles, forming a robust microstructure.
- Advanced techniques such as hot isostatic pressing or spark plasma sintering can further suppress grain growth, resulting in a nearly pore-free, highly dense structure.
- The sintered blanks require high-precision processing through diamond tool grinding, lapping, polishing, and even laser cutting to meet strict dimensional and surface finish requirements.
- The final product undergoes comprehensive testing, including density, porosity, microstructure (SEM), and mechanical properties.
Jifeng Ceramics offers alumina materials with purity ranging from 92% to 99.9%. We utilize various forming methods, including dry pressing, slip casting, isostatic pressing, injection molding, and gel casting, to meet diverse customer needs and the technical requirements of complex parts.
Jifeng Ceramics possesses atmospheric sintering, hot pressing, and internationally advanced hot isostatic pressing and pressureless sintering furnaces, as well as various precision ceramic processing and testing equipment, to meet the needs of manufacturing complex structures and high-precision parts.
With advanced processing equipment and extensive technical expertise, we can provide customers with a full range of solutions, from material selection and design optimization to customized processing, helping them obtain high-quality alumina ceramic products.
If you need to purchase alumina plates, rods, tubes, or custom-machined parts, please contact us. Our experts will be happy to assist you.
Frequently Asked Questions About Alumina Ceramics
Is alumina ceramic brittle?
Alumina ceramic is harder than most metals, but it is also more brittle by nature. This does not mean it is unreliable. In most industrial applications, proper thickness, backing design, and installation greatly reduce the risk of cracking or chipping. For high-impact areas, ceramic-metal composite designs are often used.
What alumina purity should I choose for my application?
The right purity depends on working conditions. 92% alumina is commonly used for general wear protection. 95% to 97% alumina offers a good balance of strength, wear resistance, and cost. 99% alumina is preferred for high-temperature or electrical insulation applications. Selecting the right grade helps avoid overdesign and unnecessary cost.
Can alumina ceramics replace steel or rubber liners?
Alumina ceramics can replace steel or rubber in many wear applications, especially where abrasion is the main failure mode. In systems with extreme impact or vibration, a hybrid solution combining ceramic and metal is often more effective. Material selection should always consider the full operating environment.
Where are alumina wear ceramic liners most commonly used?
Alumina wear ceramic liners are widely used in mining, power plants, bulk material handling, chemical processing, and cement industries. Typical applications include chutes, hoppers, pipelines, elbows, and areas exposed to continuous abrasive flow.
How long do alumina ceramic components typically last?
Service life depends on material grade, installation quality, and operating conditions. In many abrasive environments, alumina ceramics last three to ten times longer than traditional steel liners. This extended lifespan often reduces maintenance and downtime costs.
Are alumina ceramic parts resistant to corrosion and chemicals?
Alumina ceramics show excellent resistance to most acids, alkalis, and chemical media. This makes them suitable for corrosive environments where metal parts would suffer rapid degradation. However, compatibility should still be verified for extreme conditions.
Can alumina ceramic parts be customized?
Yes. Alumina ceramic components can be customized in material grade, size, thickness, shape, and mounting method. Customization ensures the ceramic fits the equipment correctly and performs reliably under real operating conditions.
 JiFeng Ceramics
JiFeng Ceramics
